
Reducers are part of Redux (which is a predictable state container for JS apps). Redux is used mostly for application state management in JS frameworks / libraries. Redux maintains the state of an entire application in a single immutable state tree (object) which cannot be changed directly. To change something, a new object must be created (using actions and reducers).
So what are reducers anyway ?
Reducers are used in response to an action which is sent to the store (a single immutable store). Reducers specify how the application’s state changes while action only describe what happens. You can think of reducers like an state changer, Let’s take an example of simple application where you want display list of food dishes using React js with Redux. Now, this list will usually have 3 actions:
i) DISHES_LOADING : which indicates dishes are been loading.
ii) DISHES_FAILED : which indicates the application failed to fetch the dishes details.
iii) ADD_DISHES : which indicates adding new dishes to a list.

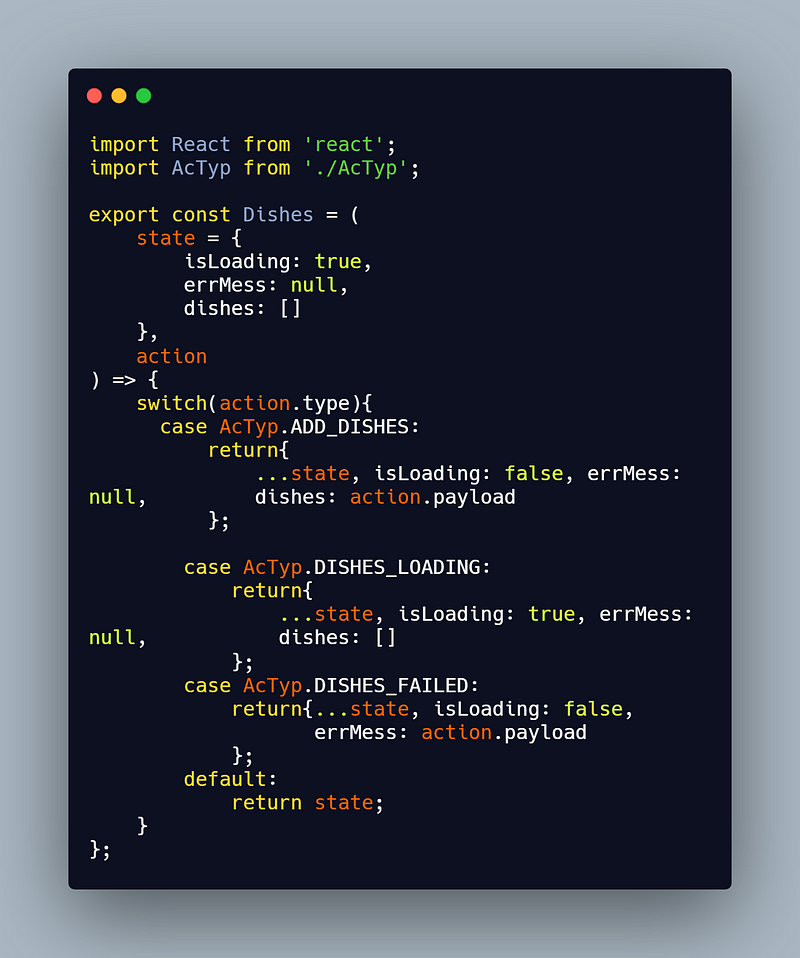
Here you can see we don’t mutate the state , we simply create a return the the new copies of the object. The default state returns the previous state.
But what if I had more than one reducer for my app?
You might need more than reducer for your app and you also want those reducers to have their results combined into a single object ( rather than different copies of the object ). Let’s take another reducer for comments:
Again, there will be three actions for comment:
i) ADD_COMMENT: which will indicate adding a new comment.
ii) COMMENT_FAILED: which will indicate comment the user was trying to put failed.
iii) ADD_COMMENTS: which will add all the comments from the store.
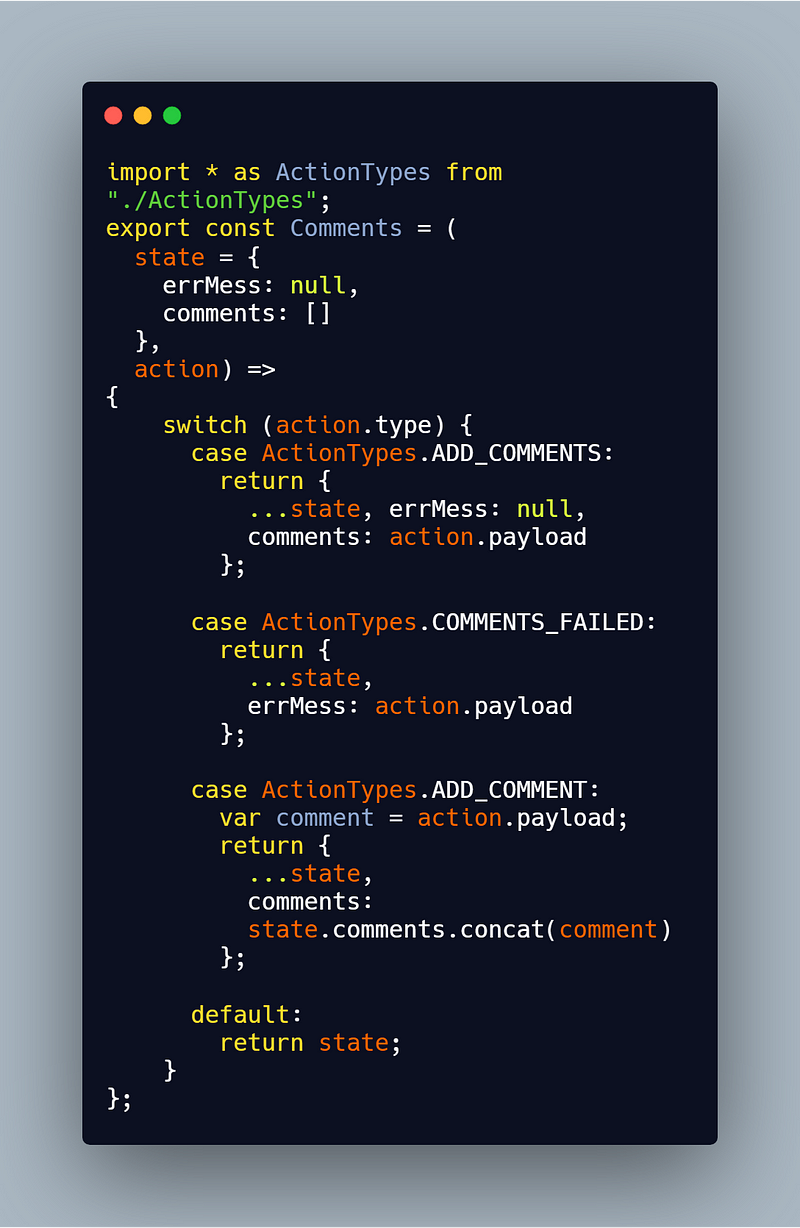
Now, we need to combine these two reducers in order to create only a single new object when there is a state change. To do that use combineReducers() which generate a function that calls your reducers with the slices of the state selected according to their keys, and combines their results into a single object again.
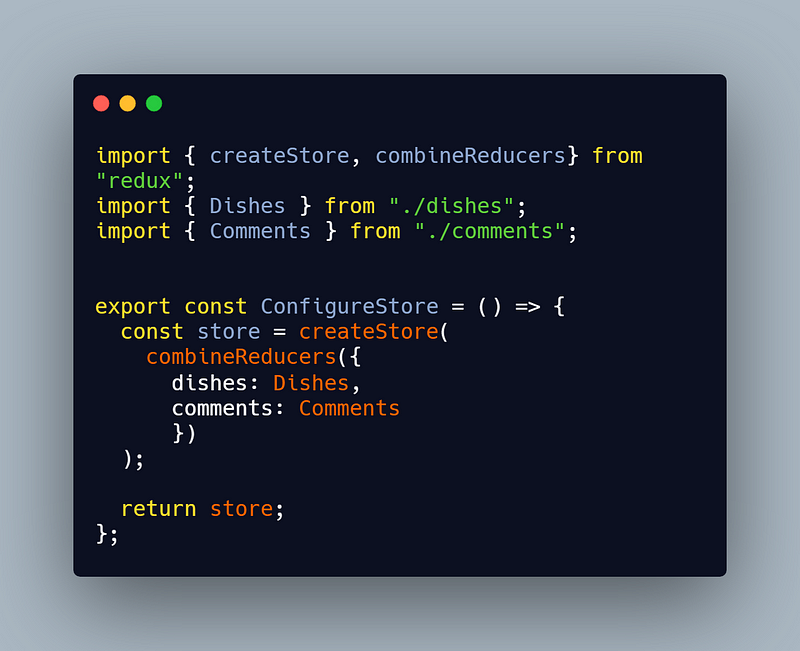
This way you can easily create a reducer for your actions for the app you are creating. Always note down the actions of your component/components before you start coding, this way you need not worry about adding new actions later on.
Thank you for reading :)

Comments
Post a Comment